Navigating the Complex Landscape of Data Brokerage Where Innovation Meets Privacy Challenges

In a world where technology evolves at lightning speed, the delicate interplay between commerce and individual rights has never been more scrutinized. Every click, every interaction online contributes to a vast repository of information, shaping advertising, services, and user experiences. However, this wealth of knowledge comes at a potential cost. While many celebrate the advancements that come from such insights, there are pressing questions about the ethical implications surrounding personal information usage.
Individuals increasingly find themselves in a precarious situation, caught between the benefits of personalized services offered by businesses and the discomfort of potential surveillance. Brands leverage informative insights to enhance customer engagement, often blurring the lines of consent and shared understanding. It becomes critical to consider who truly owns this collection of data and how it influences our daily lives, often in ways we may not fully comprehend.
As conversations flourish around regulation and responsible stewardship of sensitive information, the need for transparency has become paramount. Stakeholders, including consumers, legislators, and organizations, must navigate a complex landscape that demands both progress and protection. Striking a harmonious chord between advancement and ethical boundaries proves challenging, especially when profits and privacy are on opposing ends of the spectrum.
Ultimately, the quest for solutions continues, urging collaboration and dialogue among all parties involved. The future landscape is uncertain, yet fostering awareness and establishing trust may serve as fundamental pillars in addressing these critical issues. Only time will reveal how this story unfolds, but one thing remains clear: understanding the ramifications is essential for shaping a better tomorrow.
Overview
In modern society, entities involved in information exchange play a crucial role. They collect, analyze, and sell vast amounts of personal insights. These activities fuel many industries, creating opportunities that were previously unimaginable. Yet, the implications of this practice stir considerable debate. How much do we truly understand about the mechanisms in play? This question remains largely unanswered.
Entities involved in this field serve various purposes. They assist businesses in targeting their audiences effectively. By providing raw insights, they help organizations improve their strategies and offerings. Additionally, these intermediaries support market research, allowing companies to adapt to shifting consumer needs. However, the constant flow of information can also lead to serious challenges.
Privacy risks are inherent in the processes these entities employ. Individuals often remain unaware of how their information is gathered and utilized. Lack of transparency breeds mistrust, and this sentiment only intensifies as more people become aware of these practices. Furthermore, breaches of sensitive information can have dire consequences on personal security.
Understanding their operations is essential for both consumers and businesses. Awareness can empower individuals to make informed choices regarding their data. On the flip side, organizations can enhance their practices by prioritizing ethical standards. By fostering a culture of responsibility, stakeholders can navigate this complex environment with greater confidence and integrity.
Exploring the roles played by these entities reveals a multifaceted landscape. Each participant contributes uniquely to the overall ecosystem. Some focus on aggregating insights, while others emphasize the analysis of data trends. This diversity underscores the importance of recognizing the various functions at play.
Ultimately, comprehension of their impact paves the way for a more informed public discourse. As society evolves, so too should our perceptions and understandings of these complex relationships. By fostering dialogue, we can work towards a balance that prioritizes both innovation and individual rights.
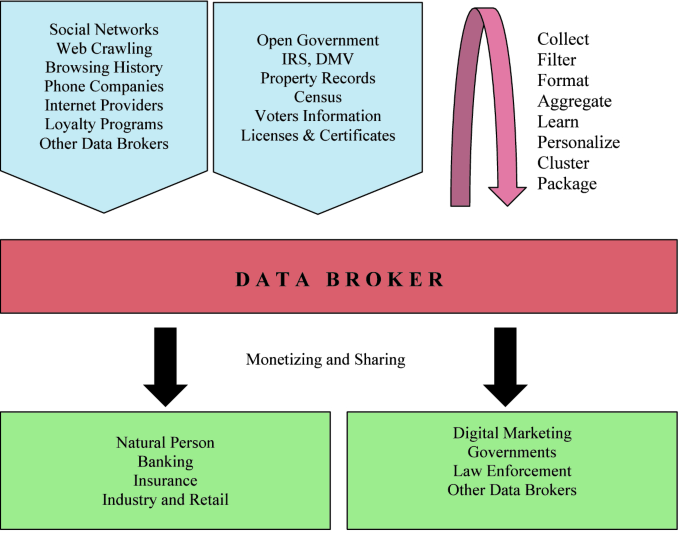
Understanding the Role of Data Brokers
In today’s digital landscape, the exchange of information plays a pivotal role in various sectors. Companies amass vast amounts of details about consumers, often without their knowledge. This practice raises critical questions. How does this accumulation of knowledge impact individuals? What are the implications for businesses harnessing such insights? These inquiries guide our exploration into the intricate web surrounding personal information utilization.
While many perceive these entities as mere middlemen, their influence extends far beyond simple transactions. These players aggregate information from numerous sources, creating comprehensive profiles that can reveal behaviors, preferences, and potential future actions. This information is not just numbers; it can dictate marketing strategies, shape product offerings, and even affect consumer choices.
- Aggregating public records
- Collecting browsing history
- Analyzing social media interactions
- Providing insights for businesses
- Enhancing targeted advertising
Understanding the mechanics behind this practice is essential. Profiles built through such extensive data collection become valuable assets for companies aiming for precision in their outreach strategies. As a result, organizations can tailor their campaigns to specific audiences, increasing engagement and conversion rates.
However, lurking beneath this surface lies a myriad of privacy concerns. Individuals remain largely unaware of the extent to which their lives are monitored. Many often find it unsettling when informed about sophisticated algorithms that predict their desires even before they realize them. The juxtaposition of convenience and confidentiality creates a complex relationship.
Moreover, this intricate ecosystem is fueled by technological advancements, making it easier to collect and analyze information. Increased connectivity and smart devices contribute significantly to this phenomenon. Data flows rapidly, presenting both opportunities and challenges. Therefore, exploring this realm necessitates a keen understanding of its multi-dimensional nature.
Privacy Risks in Data Collection
In today’s technology-driven society, vast amounts of personal information are collected every day. Individuals often unknowingly share their details through various online platforms. This collection can lead to significant privacy challenges. Many factors contribute to the growing concerns over how this information is used and stored. It’s essential to understand the implications of such practices.
Personal data can be misused in numerous ways. Unauthorized access to sensitive information can result in identity theft. Additionally, companies may sell data without proper consent. Such actions pose risks to individual privacy and trust. Consumers frequently remain unaware of how their data is handled.
Moreover, the aggregation of data can create detailed profiles. Marketers and advertisers may exploit these profiles to target individuals with tailored content. While this can enhance user experience, it raises ethical concerns. People often feel uncomfortable knowing that their interests are monitored closely. Transparency in data practices is increasingly demanded by the public.
The complexity of privacy regulations further complicates the issue. Different jurisdictions impose varying requirements for data handling. This disparity can create loopholes that exploit consumers’ rights. For instance, a company operating in multiple countries might not fully comply with all regulations. As a result, users become vulnerable to violations without realizing it.
| Privacy Risks | Explanations |
|---|---|
| Identity Theft | Unauthorized access leading to financial loss and personal harm. |
| Invasive Marketing | Targeted advertising based on extensive profiling and tracking. |
| Lack of Transparency | Consumers often remain uninformed about data usage practices. |
| Regulatory Confusion | Complex laws across regions create challenges for compliance. |
Understanding these risks is crucial for individuals and organizations alike. Protecting personal information while utilizing it for business purposes is challenging. Thus, a balanced approach must be established. This way, both privacy and practical advantages can coexist without compromising trust.
Regulatory Landscape Surrounding Data Brokers
Understanding the regulatory framework is crucial for any industry involved in personal information management. This environment shapes the practices and operations of organizations that handle consumer data. Laws often emerge in response to growing concerns about privacy and security. As technology advances, so do the regulations meant to protect individuals. Keeping pace is essential for compliance.
Numerous regulations exist across various jurisdictions, impacting how organizations can collect and utilize information. For instance, GDPR in Europe set a high standard, emphasizing consumer consent and data protection. Similarly, the CCPA in California provides residents with specific rights regarding their personal data. These frameworks reflect a shift towards greater accountability among entities that manage sensitive information.
| Regulation | Region | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| GDPR | European Union | Consumer consent, right to access, data portability |
| CCPA | California, USA | Right to know, right to delete, opt-out options |
| PIPEDA | Canada | Accountability, transparency, individual access rights |
| HIPAA | USA | Protected health information, strict security standards |
Compliance with these regulations is not optional; it is imperative. Organizations face severe penalties for violations, emphasizing the need for robust governance structures. Adapting to this evolving landscape requires strategic planning and ongoing education. Businesses must prioritize the ethical use of data to foster trust and maintain consumer relationships.
In addition to compliance, regulations offer an opportunity for improvement. They encourage organizations to adopt best practices that enhance data security measures. Streamlined processes lead to operational efficiencies, significantly benefiting the overall consumer experience. Staying ahead of regulatory changes can become a competitive advantage in a crowded marketplace.
As stakeholders push for stronger protections, new regulations will likely emerge. The conversation around privacy is ongoing, and businesses must remain vigilant. Engaging with policymakers can help shape future laws in ways that support innovation while safeguarding consumer interests. Ultimately, a proactive approach to regulation not only ensures compliance but also demonstrates a commitment to ethical practices in data management.
Regulatory Landscape Surrounding Data Brokers
In recent years, the collection and utilization of personal information have attracted significant attention. Concerns about user privacy are growing. Yet, the benefits of information sharing cannot be overlooked. Regulatory frameworks are evolving to address these challenges. Different regions and countries are implementing various approaches.
Navigating this complex legal environment is vital for organizations involved in information trading. Some countries have adopted stringent measures to protect consumers, while others take a more laissez-faire stance. For instance, the European Union implemented the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), a comprehensive law that sets a high standard for data protection and mandates transparency in data handling practices.
Conversely, in the United States, the approach is more fragmented. Various states enacting their own legislation leads to a patchwork of regulations. This inconsistency can create confusion among businesses striving to comply with different sets of rules. Moreover, federal legislation is still in the works, further adding to the uncertainty.
Consumer rights are also at the forefront of discussions surrounding these regulations. Individuals want more control over their own information. They seek clarity on how their data is collected, shared, and used. For example, many states in the U.S. are passing laws to allow individuals to opt out of information sales. This movement is indicative of a broader push for enhanced consumer agency.
Additionally, ethical considerations play a crucial role in shaping the regulatory environment. Organizations are increasingly being held accountable for their practices. While compliance is essential, ethical behavior should be seen as a competitive advantage. As consumers become more aware of their rights, businesses must prioritize transparency and responsible stewardship of personal information.
Ultimately, the regulatory landscape continues to evolve, influenced by technological advancements and public sentiment. Stakeholders must remain vigilant and adaptable. Only through active engagement with regulatory developments can companies navigate the complexities of this dynamic environment successfully.
Consumer Awareness and Data Rights
In today’s interconnected world, individuals must navigate the complexities of personal information usage. Awareness about how information is collected, shared, and utilized has never been more critical. As technology advances, the potential for misuse rises along with the necessity for informed consent. People deserve to understand their rights regarding personal data and the implications of data handling practices.
Many are unaware of the extent of information being gathered. Details such as browsing habits, purchasing preferences, and even social interactions are often captured without explicit consent. This lack of transparency can lead to discomfort and mistrust. Moreover, individuals may find it challenging to exercise their rights without proper knowledge.
Consumers should be equipped with knowledge about their choices. Understanding what data is collected allows individuals to make informed decisions. Here are some key rights that everyone should know:
- Right to Access: Individuals can request access to their personal data.
- Right to Rectification: Users can seek correction of inaccurate information.
- Right to Erasure: Also known as the “right to be forgotten,” this allows consumers to demand deletion of their data.
- Right to Data Portability: Users have the right to transfer their data between service providers.
- Right to Object: Individuals can refuse processing of their data under certain conditions.
Each right plays a vital role in protecting individuals within this digital ecosystem. However, the effectiveness of these rights often hinges on consumer knowledge. Many people lack the tools to navigate privacy policies. Complex terms and conditions can deter individuals from asserting their rights. Thus, it’s crucial to advocate for simplified communication regarding privacy practices.
Moreover, education about these rights can empower users to take control of their personal information. Understanding the implications of consent is essential. It’s not just about agreeing to terms; it’s about recognizing the long-term impact on privacy. Increasing awareness can lead to a more proactive approach toward personal information management.
In conclusion, fostering awareness is paramount in this era of information. With knowledge, individuals can champion their rights effectively. The balance between technology and privacy requires active participation from consumers. As awareness grows, the dialogue surrounding responsible data usage will continue to evolve.
Ethical Considerations in Data Usage
In a rapidly evolving digital landscape, the ethical dimensions of information utilization have gained immense importance. The collection and processing of detailed user profiles can lead to significant benefits, but these advantages must be carefully weighed against moral implications. Consumers often remain unaware of the extent of data gathering practices. Transparency is key in fostering trust. Moreover, ethical practices should guide how organizations handle personal information.
With the advent of technology, new challenges emerge, particularly concerning consent and autonomy. To what extent do users genuinely understand what they agree to when they consent to data collection? This uncertainty raises pressing questions about informed consent, as often, individuals are not fully aware of the ramifications associated with sharing their information.
Furthermore, the issue of fairness in data usage cannot be overlooked. Certain demographics may be disproportionately affected by targeted marketing strategies or predictive analytics, leading to unintended harm or exclusion. This suggests that ethical considerations must extend beyond mere compliance with regulations and encompass broader societal impacts. Organizations must strive to ensure equitable treatment across all customer segments.
| Ethical Consideration | Description |
|---|---|
| Informed Consent | Ensuring individuals understand and agree to data usage practices. |
| Transparency | Clear communication regarding data collection and processing methods. |
| Fairness | Avoiding discriminatory practices in data application and analysis. |
| Accountability | Organizations must be held responsible for data misuse. |
Ethical dilemmas are also frequently encountered in the realm of accountability. Companies must be held responsible for potential misuse of personal information, and failure to act responsibly can result in significant consequences, both legally and reputationally. Organizations should implement strong governance frameworks that guide ethical decision-making, promoting responsible practices throughout their operations.
Ultimately, the ethical considerations surrounding information usage are multifaceted and complex. As technology advances, continuous dialogue is essential to navigate the evolving landscape. Striking a balance between innovation and ethical responsibility will define the future of information practices.
Impact on Marketing and Advertising
In recent years, evolution in technology has transformed how businesses approach their marketing strategies. Companies are now able to gather extensive insights into consumer behavior. This has led to targeted advertising becoming more personalized and efficient. However, this new landscape also comes with its own set of challenges. Organizations must navigate the fine line between utilizing consumer information and respecting individual privacy.
Access to vast amounts of consumer insights allows brands to tailor their messaging. Advertisements can now reach specific demographics with unprecedented accuracy. This precision not only enhances customer experience but drives higher conversion rates. Utilizing advanced algorithms, marketers analyze data patterns to predict future purchasing behaviors. As a result, campaigns can be crafted that resonate more deeply with potential customers.
However, challenges arise with such detailed profiling. Questions emerge about consent and transparency in data usage. Many consumers remain unaware of how their information is collected and employed. Issues surrounding privacy are gaining traction, prompting businesses to reconsider their strategies. While data-driven marketing offers numerous advantages, a delicate balance must be maintained to ensure trust and credibility.
Furthermore, effective regulation is crucial to protect consumer rights while allowing companies to thrive. Communities are increasingly demanding accountability from organizations regarding their data practices. Striking the right equilibrium can yield benefits for both brands and consumers alike. Organizations that prioritize ethical practices will likely foster stronger customer loyalty over time.
Meanwhile, advancements in technology also play a significant role. With tools such as artificial intelligence, automation has revolutionized campaign management. Advertisers can optimize their strategies in real-time, adjusting messages to align with changing consumer preferences. This agility not only enhances marketing efforts but also provides a smoother experience for consumers. Additionally, innovations in data security are paramount. As firms adopt new technologies, they must ensure that consumer information is safeguarded from breaches.
Looking ahead, the evolution of marketing will continue to shift. Emerging technologies will undoubtedly transform how brands interact with their audiences. As automated systems analyze more complex datasets, personalization will reach new heights. However, the importance of ethical considerations cannot be overstated. The industry must adapt to ensure that trust remains at the forefront of consumer relationships.
Technological Advances and Data Security
In today’s rapidly evolving landscape, the intersection of technology and personal information is more critical than ever. With advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and blockchain, companies are exploring innovative ways to collect and use consumer information. However, this progress brings with it significant challenges regarding the protection of individual privacy. Organizations face a dual responsibility: fostering innovation while ensuring the confidentiality of sensitive data. The balance is delicate, but essential for maintaining consumer trust.
A multitude of tools are available to enhance security measures. From encryption to anonymization techniques, businesses are increasingly deploying advanced solutions. These methods not only protect personal information but also create a sense of assurance among users. As technologies become more sophisticated, so too do the strategies to safeguard data against breaches. High-profile incidents have underscored the urgency of fortifying security protocols.
One key area of focus is artificial intelligence. Machine learning algorithms analyze vast amounts of information to identify potential threats. By predicting malicious activities, companies can respond proactively rather than reactively. This shift from a defensive to an offensive strategy represents a significant leap in security practices. However, reliance on AI must be tempered with ethical considerations, as algorithms can sometimes inadvertently perpetuate biases.
Moreover, blockchain technology offers exciting possibilities for enhancing transparency. A decentralized ledger can provide an immutable record of transactions, promoting accountability in information handling. Consumers can gain greater insight into how their data is used and shared, fostering a culture of trust. This technological innovation empowers individuals, additional resources allowing them to take control of their own information.
Privacy regulations are evolving alongside these technologies. Governments are increasingly recognizing the need for robust frameworks to protect consumer rights. Laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe set standards for data handling practices. Compliance with such regulations poses challenges but also drives improvements in security measures across industries.
As we look to the future, it is evident that technological advancements will continue to shape the landscape of information security. Organizations must remain vigilant, adapting to new threats while embracing emerging solutions. In this dynamic environment, the focus should remain on creating sustainable practices that prioritize individual privacy without stifling innovation.
| Technology | Application | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Artificial Intelligence | Threat Detection | Proactive security measures |
| Blockchain | Data Transparency | Enhanced trust and accountability |
| Encryption | Data Protection | Safeguarding sensitive information |
| Anonymization | User Privacy | Reducing risk of data exposure |
Ultimately, the future holds immense potential for blending technological advances with security initiatives. By prioritizing ethical practices and regulatory compliance, organizations can foster an environment where innovation and privacy coexist harmoniously. As we navigate this complex terrain, the commitment to protecting personal information remains paramount.
Future Trends in Data Brokerage
As technology evolves, the landscape of information exchange continues to transform remarkably. Emerging trends reveal both exciting opportunities and complex challenges. The future promises advancements in analytics, privacy solutions, and consumer engagement strategies. With each new development, new questions arise about ethics and responsibility.
One major shift will be the increasing reliance on artificial intelligence. AI can streamline data processing and provide deeper insights into consumer behavior. This shift will likely enhance personalization in marketing campaigns, leading to improved user experiences. However, as algorithms become more sophisticated, transparency in their functioning will become crucial.
Another aspect worth noting is the growing emphasis on user consent. As privacy regulations tighten, companies must prioritize explicit permission when collecting personal information. This approach fosters trust between organizations and individuals. Moreover, it underscores the need for clear communication about how data is utilized. The expectation is that informed consent will empower users, allowing them to control their information.
Blockchain technology is also poised to play a significant role in future transactions involving personal information. Its decentralized nature can enhance security and accountability. Leveraging blockchain can mitigate risks of data breaches while providing a transparent means of tracking how information is exchanged or sold. This shift could redefine ownership rights and privacy, leading to a more equitable landscape.
Moreover, as consumers become more aware of their rights, they will demand greater accountability from companies. Public pressure can catalyze the adoption of ethical practices in data handling. Businesses that align with consumer values on privacy will likely gain a competitive edge. Social responsibility will not just be a buzzword; it will be a key differentiator in the marketplace.
Lastly, the integration of advanced technologies such as machine learning will pave the way for more effective segmentation and targeting. However, with this power comes the responsibility to ensure that such strategies do not infringe on ethical boundaries. The balance between customization and respect for individual privacy will remain a significant challenge. Thus, organizations must navigate this complex terrain thoughtfully, ensuring sustainable practices for the long term.

