Exploring the Hidden Implications of Privacy Policies in the World of Data Brokers

In an age where personal information is more valuable than ever, the role of intermediaries becomes increasingly significant. These entities specialize in collecting, analyzing, and distributing myriad details about individuals. Often unnoticed, they operate behind the scenes, influencing how personal insights are managed. The complexity is profound, as their activities can affect privacy in ways that are not readily apparent to the average consumer. Understanding this landscape requires delving deeper into the nuances and implications of their operations.
Many users remain blissfully unaware of how their information is utilized. Surprising as it may seem, everyday actions contribute to a vast repository of data that fuels a hidden market. The intricacies of this ecosystem can seem overwhelming. However, it’s essential to grasp the intricacies involved. This practice not only raises ethical concerns but also prompts a critical examination of the safeguards in place.
Within this framework, transparency is often lacking, leaving individuals in the dark about who accesses their data and for what purposes. There is a delicate dance between convenience and confidentiality, as many individuals willingly exchange personal details for enhanced user experiences. Yet, amidst this trade-off lies a pressing question: at what cost do these benefits come? Engaging with this reality requires a keen eye and an inquisitive mind.
Effective scrutiny of these operations demands an understanding of the fine print that often accompanies various agreements. Every checkbox checked, every permission granted is a potential doorway to more profound implications. As users, being aware of the subtleties in these documents can empower individuals to make informed decisions. Ultimately, the quest for privacy in a world teeming with information and technology remains an ongoing challenge that warrants attention and action.
Understanding Data Brokers’ Role
In today’s digital landscape, entities play a vital role in the ecosystem of information exchange. These organizations collect various details, often without the individual’s knowledge. Their influence stretches into multiple sectors, impacting how personal information is utilized. Consumers rarely grasp the extent of this practice.
Entities gather a multitude of information types. They utilize advanced technology and analytics to process data efficiently. This allows them to create comprehensive profiles that can be sold or used for targeted marketing. Such profiles can contain everything from demographics to purchasing behaviors.
- Contact information
- Social media profiles
- Financial records
- Health-related data
- Consumer preferences
Individuals may not be aware that their online activities contribute significantly to this collection. Every click, like, and share can be meticulously tracked. This unceasing flow of information shapes the market and influences advertising strategies.
Moreover, the types of details harvested go beyond mere superficial traits. For instance, sensitive and personal information can be bundled with general statistics. Such an aggregation can lead to unexpected consequences, especially when used for targeted campaigns or even discrimination.
In essence, these organizations operate as intermediaries, providing insights that can be immensely valuable for businesses. However, the consequences of their actions often remain hidden from consumers, who may unwittingly become part of a much larger data narrative.
Ultimately, understanding the scope and nature of the information collected is essential. By grasping this reality, individuals can begin to navigate their digital presence more thoughtfully. Awareness empowers consumers, allowing them to take control of their personal data in an increasingly interconnected world.
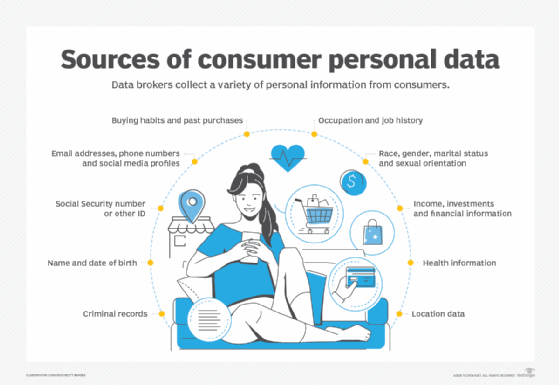
Types of Data Collected by Brokers
In today’s interconnected world, various entities gather extensive information about individuals for different purposes. This information can be incredibly diverse and often includes details that many might consider personal. The range of data collected is vast, encompassing everything from basic identifiers to behavioral patterns. Understanding what kind of details are being amassed helps illuminate the broader implications for personal security.
Some common identifiers include names, addresses, and phone numbers. Online activity is another significant source of information. This includes browsing habits, purchases, and social media interactions. Such details form a rich tapestry that can reveal much about a person’s lifestyle.
Additionally, financial records and credit histories are often part of the equation. Such sensitive information can drastically impact one’s financial opportunities and risks. Employment history also features prominently, encompassing job titles, durations of employment, and even salary figures. When aggregated, these details can paint a clear picture of an individual’s economic status and spending habits.
Moreover, health-related information, although more regulated, can find its way into collection efforts. Consumer preferences, expressed through surveys or loyalty programs, contribute to this growing repository of knowledge. Location data, often derived from mobile devices, adds another layer of complexity. This geolocation information helps identify where a person spends their time, further contextualizing their behavior.
In essence, the variety of information collected is staggering and can include intimate facets of life that one may not even consider relevant to others. Such exhaustive datasets, when analyzed, yield insights that can be both advantageous for businesses and unsettling for individuals, as they often lack awareness of the extent of the surveillance. Keeping track of all this information is no small challenge, and it raises critical questions about consent and awareness in an era dominated by technology.
How Privacy Policies Are Structured
Understanding the framework of agreements regarding personal information is essential. These documents can often feel overwhelming. They outline how organizations handle what is shared. It’s crucial to grasp their structure for better comprehension. Many individuals overlook key elements present in these statements.
Typically, these documents start with an introduction. Here, the organization often explains its commitment to safeguarding information. This is followed by detailed sections that elaborate on various topics. From collection methods to usage purposes, clarity is essential. However, the terminology can be convoluted and filled with legal jargon.
Next, policies usually cover types of information gathered. This includes both personal identifiers and broader data sets. Many individuals may not realize the extent of what is collected. For instance, this could range from demographic details to online behaviors. It’s vital to note that sometimes, data is acquired from third parties as well.
| Section | Description |
|---|---|
| Introduction | Overview of the organization’s commitment to information protection. |
| Information Collection | Details on what types of information are gathered and how. |
| Usage of Information | Explanation of how the collected data is utilized within the organization. |
| Sharing Practices | Information on whether the data is shared with third parties. |
| Consumer Rights | Details on what rights consumers have regarding their data. |
Following the collection details, there is often a section dedicated to usage. Organizations outline the purposes behind the data gathering. This can include improving services or tailoring marketing efforts. Yet, consumers frequently underestimate how deeply this affects their experience. Such practices are often justified by a promise of enhanced user interaction.
Another significant aspect is how shared data is handled. When it comes to partnerships or affiliations, transparency can be lacking. Companies may transfer information to third-party entities. They often claim it’s for analytics or service improvement. However, the implications of such sharing can be far-reaching.
Moreover, rights concerning individual data are crucial. Good agreements will elucidate what consumers can do. This could involve options to access, correct, or delete their information. However, it’s not always straightforward, and many remain unaware of these rights. Organizations may also include disclaimers regarding potential changes over time.
Finally, concluding sections typically address modifications. These updates often inform users about the evolving nature of agreements. Some notices may feel hidden, making them easy to overlook. Consumers should remain vigilant and regularly review such documents to stay informed. Awareness is key in navigating these complex structures.
Key Players in the Data Brokerage Industry
The realm of information trading is a complex web of players, each contributing to the vast ecosystem of personal information exchange. Understanding who these key participants are is crucial for grasping the dynamics of this field. There are significant entities, ranging from large corporations to small startups, that all play pivotal roles. The impact of their activities stretches far beyond mere transactions.
- Large Corporations: Major companies often dominate the market.
- Small Startups: Innovative newcomers are frequently disrupting traditional practices.
- Technology Giants: These firms possess extensive resources for collection and analysis.
- Market Research Firms: They provide insights based on aggregated information.
In this intricate industry, notable players like tech conglomerates utilize advanced algorithms to compile extensive profiles, capturing consumer behavior on an unprecedented scale. Meanwhile, smaller companies seek to carve out niches by offering specialized services. Various firms focus on specific sectors, catering to distinct client needs.
- Advertisers
- Financial Institutions: They analyze consumer habits to mitigate risks.
- Healthcare Providers: They utilize information for research and patient engagement.
Through strategic partnerships and collaborations, these organizations enhance their capabilities, pooling resources and insights to create comprehensive databases that significantly benefit their clientele. Transparency, however, often takes a backseat, raising questions about ethical practices.
In conclusion, recognizing these influential players offers valuable insights into how individual information is collected, analyzed, and utilized. The interplay of various entities shapes the operational landscape, impacting consumers and businesses alike.
Consumer Rights and Data Protection
In an age where information is a powerful commodity, individuals must understand their entitlements. Many people are unaware of the extent to which their personal information is collected and shared. This lack of awareness can lead to vulnerabilities. It’s critical to acknowledge that each person has rights. These rights empower consumers and provide a framework for protection against misuse.
Legislation plays a pivotal role in defining these rights. Various laws are designed to ensure individuals can access, correct, or delete their personal information. Moreover, transparency is key. Entities that collect personal information are often required to inform users about their practices. However, this process can be convoluted and difficult to navigate.
Consumers often face an uphill battle. Not all information is easily accessible or understandable. The language used in documentation can be complex. This puts individuals at a disadvantage when trying to assert their rights. For instance, many might not know how to request their information, let alone challenge inaccuracies.
In recent years, several measures have been introduced to enhance protection. These include stricter regulations and improved enforcement mechanisms. Nonetheless, challenges persist. Some companies may employ loopholes to skirt regulations. Additionally, the rapid evolution of technology complicates the regulatory landscape.
Awareness is crucial. Consumers should remain informed about their rights. Engaging with advocacy groups can provide valuable insights. Additionally, individuals can monitor their own information. Proactive steps can help in safeguarding personal data. Ultimately, understanding one’s rights is a vital first step in the journey toward better protection.
The responsibility does not solely lie with consumers, however. Organizations must also prioritize ethical practices. They need to implement transparent processes. Cooperation between entities and individuals can lead to a more secure environment. Balancing interests will require continuous dialogue and reform.
Challenges in Regulating Data Brokers
The landscape of personal information collection is both vast and intricate. Individuals often remain unaware of how their information is utilized or who holds it. Those involved in this field operate in shadows, making oversight difficult. The complexity arises from the variety of sources and methods used to gather insights about individuals. As a result, establishing effective regulations poses numerous obstacles.
One significant challenge is the constant evolution of technology. Innovations can outpace legislation, leaving loopholes that exploit individuals’ details. Additionally, the sheer volume of entities engaged in collecting information complicates enforcement. These players range from large corporations to small operations, each with different practices. Some operate within legal parameters, while others blur the lines.
Another issue is the vague nature of consent. Consumers often agree to terms without fully understanding them. Even if individuals attempt to take control, the semantics used can be deceptive. For instance, what appears as straightforward language may conceal complex agreements. This ambiguity clouds accountability, complicating any legal recourse.
Moreover, jurisdictions vary, leading to inconsistencies in how personal information is protected. What is permissible in one region may be restricted in another. This fragmentation creates a patchwork of rules that are challenging to navigate. Without a unified approach, individuals may find themselves inadequately shielded.
In addition, the secretive operations of these entities make transparency a significant hurdle. Often, companies do not disclose how they gather or utilize details. This lack of openness nurtures distrust, as consumers feel powerless over their own data. Consequently, regulations struggle to keep pace with the rapid advancements in technology and practices.
Lastly, consumer awareness plays a crucial role. Many individuals remain oblivious to the extent of their data being shared. Efforts to educate and empower consumers are essential but often fall short. If the general public cannot grasp the implications, regulations may be ineffective. Therefore, fostering an informed populace is paramount in navigating this ever-evolving domain.
Impacts on Personal Privacy
In today’s digital landscape, safeguarding personal information has become increasingly complex. The collection and usage of individual details can lead to unintended consequences. Our lives are intertwined with various technologies, making us vulnerable to exposure. With every click and online interaction, a wealth of information is generated. This constant flow of data creates a unique challenge for Learn more on Medium maintaining confidentiality.
Individuals often underestimate how much their information is shared and utilized. It’s not just about names or addresses; it encompasses behaviors, preferences, and habits. When this information is aggregated, it paints a comprehensive picture of one’s life. This can have real-world implications, influencing how individuals are perceived and treated.
Moreover, the effects on personal welfare can be profound. From targeted advertisements to surveillance, the reach of collected information is extensive. The lack of transparency surrounding these practices contributes to feelings of uncertainty. Many people wonder who has access to their data and how it is being utilized. This lack of clarity fosters distrust and anxiety.
As individuals navigate this intricate web, they often face dilemmas. On one hand, sharing information can enhance convenience and personalization. On the other hand, it raises questions about consent and control. The balance between benefits and risks is delicate. When exploitation occurs, it can lead to significant repercussions, not just for individuals but society at large.
Consequently, we must recognize the broader implications of information collection. The relationship between individuals and entities that handle their data is evolving. Awareness of these dynamics is crucial for informed decision-making. Empowering users to take charge of their information can mitigate adverse effects. Ultimately, it’s about ensuring that personal experiences are respected, valued, and safeguarded.
Strategies to Safeguard Your Information
In today’s digital landscape, protecting personal details has become increasingly crucial. With numerous avenues for information collection, individuals must be proactive. Simple measures can make a significant difference. Awareness is key. Understanding how data can be accessed and used empowers users to take charge.
First, consider your online presence. Regularly review your social media settings. Limit the information you share publicly. Avoid oversharing personal milestones or location details. Remember, even seemingly harmless posts can provide insights to prying eyes.
Secure your accounts with robust passwords. A strong password is your first line of defense. Avoid using easily guessable information, like birthdays. Instead, create unique combinations of letters, numbers, and symbols. Use different passwords for different sites to minimize risks. This practice can greatly reduce unauthorized access.
Utilize two-factor authentication whenever possible. This additional layer of security acts as a safety net. If someone manages to compromise your password, they’ll still face barriers to entry. Many platforms offer this feature, and it’s worth the extra effort. It’s a small change that can lead to significant results.
Be mindful of the information you share when filling out forms online. Only provide necessary details. Always check if a site is reputable before offering any personal data. Additionally, consider using anonymous browsing tools or VPNs to protect your location and browsing habits from third parties.
You should regularly monitor your financial statements and credit reports. Look for any suspicious activity that could indicate misuse of your information. If something seems off, act swiftly. The sooner you address potential issues, the better your chances of minimizing damage.
Educate yourself about current scams and phishing attempts. These tactics evolve constantly, and staying informed helps you recognize red flags. Be skeptical of unsolicited emails or messages requesting personal information. Always verify the source before responding or clicking any links.
Finally, consider the benefits of privacy-enhancing tools. Applications and extensions are available that can help minimize tracking. Explore options for encrypted messaging and secure email services. These technologies can create barriers against invasive practices.
By implementing these strategies, you can significantly enhance your security posture. It’s about taking ownership of your information. Every small step contributes to a larger goal. A proactive approach fosters resilience in the face of evolving threats.

